Comparison of multifrequency position measurements of compact extragalactic radio sources in the framework of the ICRF3
 Frequency-dependent position offsets (core shifts) among compact radio sources in ICRF3 (Liu et al. 2021, A&A 652, A87)
Frequency-dependent position offsets (core shifts) among compact radio sources in ICRF3 (Liu et al. 2021, A&A 652, A87)Abstract
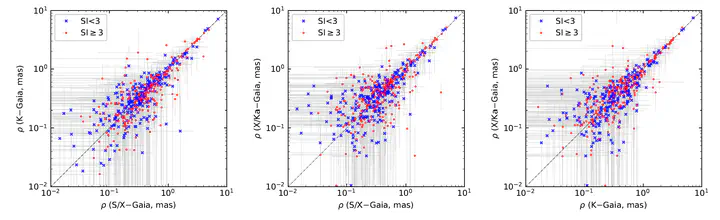
We analyzed multifrequency position measurements of compact extragalactic radio sources using very long baseline interferometry (VLBI) data within the framework of the third realization of the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF3). Positions at 8.4, 24, and 43 GHz were compared to investigate frequency-dependent offsets (core shifts) and their statistical characteristics. The results show systematic source position differences consistent with synchrotron self-absorption models, with median core shifts of 0.12 mas between 8.4 and 24 GHz and 0.06 mas between 24 and 43 GHz. Such shifts contribute to apparent source structure effects in high-frequency celestial reference frames.
Multifrequency very long baseline interferometry (VLBI) observations
enable direct investigation of the core-shift phenomenon in compact extragalactic radio sources,
providing a link between radio and optical reference frames.
Liu et al. (2021) compared source positions derived from 8.4, 24, and 43 GHz VLBI observations within the ICRF3 framework,
analyzing systematic frequency-dependent offsets and their impact on celestial reference frame consistency.
They found typical median core shifts of 0.12 mas between S/X and K bands, and 0.06 mas between K and Q bands,
consistent with the synchrotron self-absorption model of AGN jets.
These frequency-dependent shifts highlight the importance of consistent source structure modeling for future high-frequency reference frames.
Citation:
Liu, N., Liu, J.-C., & Zhu, Z. (2021). Comparison of multifrequency position measurements of compact extragalactic radio sources in the framework of the ICRF3.
Astronomy & Astrophysics, 652, A87.
https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202140656