Evaluate the ICRF3 Axes' Stability via Extragalactic Source Position Time Series
Abstract
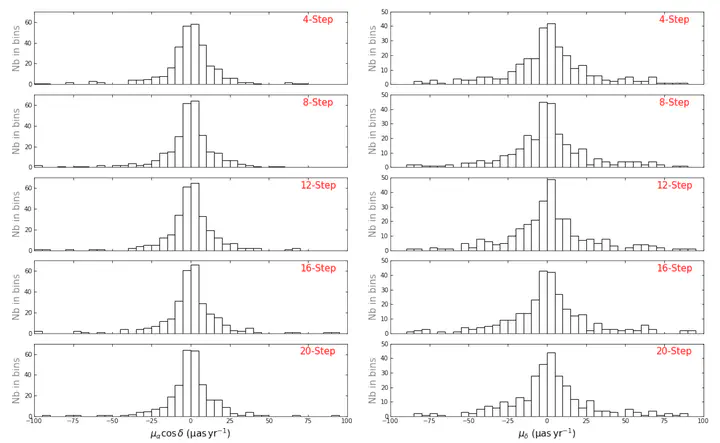
We present an updated study on assessing the axes stability of the third generation of the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF3) in terms of linear drift and scatter based on the extragalactic source position time series from analyses of archival very long baseline interferometry observations. Our results show that the axes of the ICRF3 are stable at a level of 10 to 20 microseconds of arc, and it does not degrade after the adoption of the ICRF3 when observations from new networks are included. We also show that the commonly used method of deriving the position time series (four-step solution) is robust.
Type
Publication
In International VLBI Service for Geodesy and Astrometry 2022 General Meeting